One. Power Conversion Module
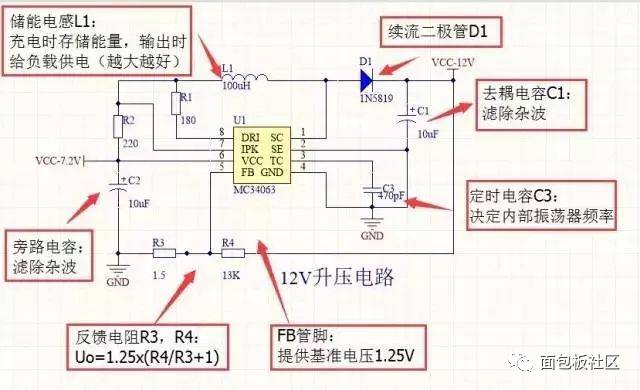
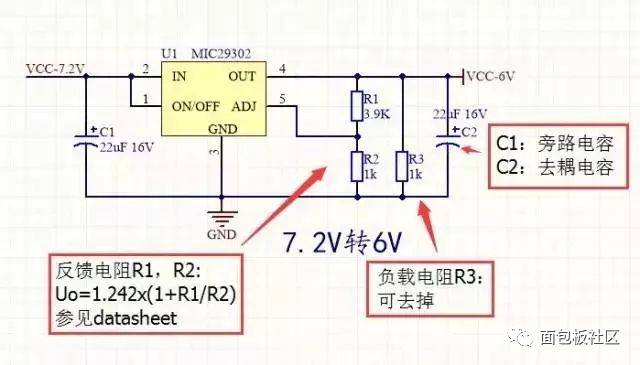
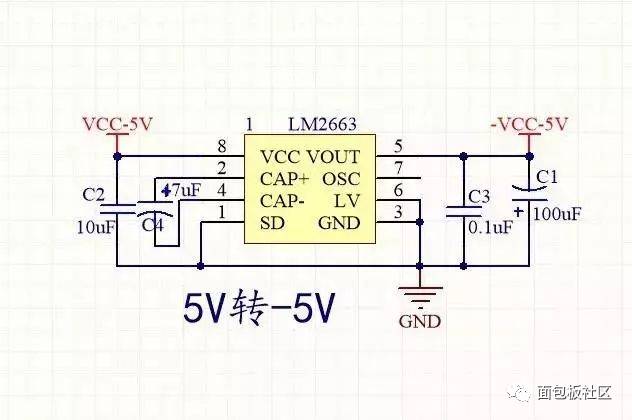
The so-called power supply voltage refers to the input voltage that is converted through a voltage conversion circuit to achieve boosting or bucking functions for other modules. In the production of smart cars, the input battery voltage is 7.2V. The required voltages for different modules are as follows: 3.3V for the minimum system board, OLED display, and Eagle Eye camera; ±5V for the operational amplifier power supply; 6V for the servo motor; 12V for the drive circuit; and 5V for the CCD and encoder. Below are some detailed explanations about the voltage conversion circuits.
Voltage regulator circuits are mainly divided into several categories:
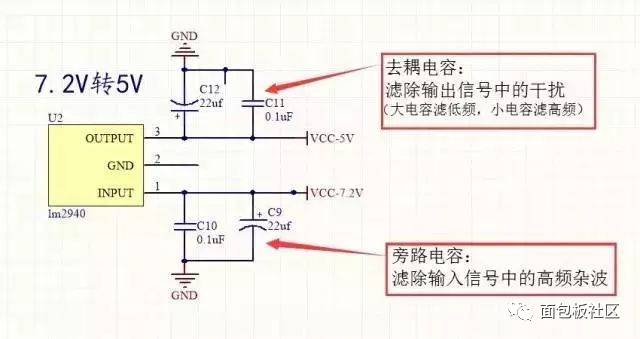
1. LM2940 to 5V:
The LM2940 is a linear regulator circuit that only supports bucking. It has a simple structure and high stability but consumes more power, occupies more space, and has lower filtering efficiency. It requires large input and output filter capacitors.

Digit Segment Led Display,Washing Machine Display,Smd Led Display,Bar Segment Led Display
Wuxi Ark Technology Electronic Co.,Ltd. , https://www.arkledcn.com