Digital video technology is widely used in communications, computers, radio and television, etc., bringing a series of applications such as conference TV, video telephony, digital TV, and media storage. Digital signals have many advantages, but when the analog signals are digitized, their frequency bands are greatly widened. After digitizing 6 MHZ ordinary TV signals, the digital rate will be as high as 167 Mbps, which requires a large amount of memory, and the occupied bandwidth will reach 80 MHz. z or so, this will make the digital signal lose its practical value. The digital compression technology solves the above difficulties well. The frequency band occupied by the compressed signal is much lower than the frequency band of the original analog signal. Therefore, the digital compression coding technology is a key technology for making the digital signal practical. The following is a discussion on the EN2200-M encoder and digital TV source codec technology and application after the transformation of the digital microwave transmission system of Changzhi microwave station.
This article refers to the address: http://
1 Digital TV coding overview
The process of encoding and quantizing an analog signal into a binary digital signal is called A/D conversion. The resulting signal is also called PCM signal. PCM coding can be performed directly on the color full TV signal, or on the luminance signal and two. The color difference signals are separately performed. The former is called full television signal coding, and the latter is called component coding. This is the most basic coding form. Digital compression coding technology can be divided into two categories: lossless compression and lossy compression. Lossless compression means that the original signal can be recovered after compression. Lossy compression cannot be restored after decompression, and there is a certain distortion, but the distortion is below a certain limit. People can't feel it. Currently, there are several compression coding methods: (1) statistical coding, such as Huffman coding and run length coding; (2) predictive coding, such as difference coding, intra prediction, inter prediction, motion compensation prediction, etc. (3) transform coding, such as DCT transform, wavelet transform; (4) quantization techniques, such as uniform quantization, non-uniform quantization and adaptive quantization techniques; (5) coding based on visual objects; (6) scalable coding. The first four coding techniques are mainly used for MPEG-2. The DVB digital television system specifies the compression coding method using MPEG-2, which is a memory-based frame-based compression method. The latter two methods are mainly used for MPEG-4. MPEG-4 is mainly used in digital TV systems for streaming digital TV.
2 Digital TV Encoder Structure
MPEG-2 compression encoder is a front-end device for MPEG-2 compression encoding and output real-time TS stream of analog TV video and audio signals. It is suitable for digital TV transmission or front-end source coding, as well as conference TV, distance education and other applications. The advanced encoder not only has a DVB interface, but also has a telecommunications interface, so that the device can be easily applied in HFC networks, microwave MMDS or 8GHZ systems, SDH or PDH networks, as shown in Figure 1.
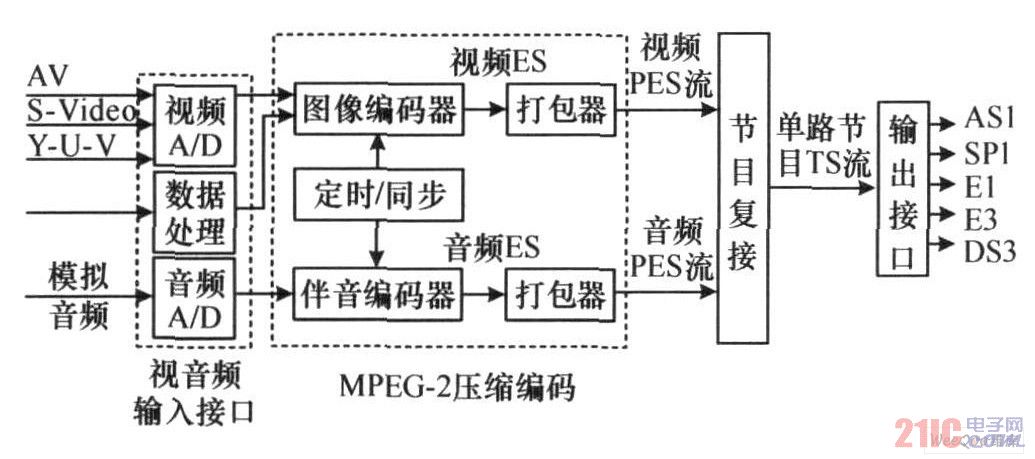
Figure 1 Block diagram of the encoder.
3 MPEG-2 video coding system and key technologies
The principle of MPEG-2 image compression is to take advantage of two characteristics in the image: spatial correlation and temporal correlation. Any scene in a frame of image is composed of several pixels, so a pixel usually has a certain relationship with brightness and chrominance of some pixels around it. This relationship is called spatial correlation; One of the plots is often composed of a sequence of images consisting of several consecutive frames of images. There is also a certain relationship between the images of the preceding and succeeding frames in an image sequence. This relationship is called temporal correlation. These two correlations make a large amount of redundant information in the image. If we can remove the redundant information and only keep a small amount of non-related information for transmission, the transmission frequency band can be greatly saved, and the receiver uses these non-related information. According to a certain decoding algorithm, the original image can be restored under the premise of ensuring a certain image quality. A good compression coding scheme can remove redundant information in the image to the utmost extent.
The coded pictures in MPEG-2 are classified into three types, which are called I frames, P frames, and B frames.
The I frame image adopts the intra coding method, that is, only the spatial correlation in the single frame image is utilized, and the time correlation is not utilized. The I frame is mainly used for the initialization of the receiver and the acquisition of the channel and the switching and insertion of the program. The compression ratio of the I frame image is relatively low, the I frame image periodically appears in the image sequence, and the frequency of occurrence can be selected by the encoder.
P-frame and B-frame images use inter-frame coding, which uses both spatial and temporal correlation. The P frame image uses only forward time prediction, which can improve compression efficiency and image quality. The P-frame image may include intra-coded portions, that is, each macroblock in the P-frame may be forward prediction or intra-frame coding. The B frame image uses bidirectional time prediction, which can greatly increase the compression factor. It is worth noting that since the B frame image uses the future frame as a reference, the transmission order and display order of the image frames in the MPEG-2 encoded code stream are different.
The encoded stream of MPEG-2 is divided into six levels. To better represent the encoded data, MPEG-2 uses a syntax to define a hierarchical structure, which is divided into six layers, from top to bottom: image sequence layer, image group (GOP), image, macroblock, macro Block, block. The main applications of the MPEG-2 standard are as follows: preservation of video and audio data; nonlinear editing systems and non-linear editing networks; microwave, satellite, optical cable transmission; broadcast of television programs.
4 Digital TV source codec technology
In all-digital TV technology, there are two very important coding technologies, namely source coding and channel coding. They use MPEG-2 technology. The main task of source coding is to solve the problem of image signal compression and preservation. Channel coding The main task is to solve the problem of image signal transmission. The amount of data of the image signal is large. If it is not compressed, the digital television signal cannot be transmitted in real time, and the main way of compression is to remove the redundant signal. The so-called redundant signal refers to those extra parts that are not related to information or have little effect on image quality. This is the principle of MPEG-2 image compression.
(1) Spatial redundancy. An image consists of hundreds of thousands of pixels. There is a great similarity (or correlation) between two adjacent pixels or even a few pixels. When transmitting, there will be a case where many identical data are continuously transmitted. Spatial redundancy, using some coding method (such as orthogonal transform coding), removes redundant information in space, and reduces transmission and recording rate.
(2) Time redundancy. TV images also have a strong time correlation. For 25 frames/s images, the difference between the previous frame and the next frame is usually small, and most of the images are the same, which indicates the adjacent two images. The correlation is very large, and the correlation of the images is gradually reduced when the images are far apart, and the highly correlated image changes are generally regular, that is, each image The changes are predictable. By using the temporal redundancy of the image, the redundant information of the image signal in time is removed, and the transmission and recording rate can also be reduced.
(3) Statistical redundancy. The image and sound signals are digitized and follow a certain statistical law. For example, under the image predictive coding system, the predicted value of the current pixel signal is predicted by the previous several adjacent pixel values ​​or the time value of the pixel on the previous segment. According to the spatial correlation and temporal correlation of the image, it is known that the probability of occurrence of a signal with a small prediction error is large, and on the contrary, the probability of occurrence is small. The statistical coding method is used to use a short code for a small error signal value with a high probability of occurrence, and a long code for a large error signal value with a small probability of occurrence, thus removing statistically redundant information of the signal.
(4) Perceptual redundancy. Human audiovisual organs have some insensitivity. Perceptual redundancy refers to video and audio signals that are insensitive or unreachable to people's visual and auditory resolution. For these insignificant information, large distortion processing is given, and people do not obviously feel the degradation of image and sound quality. Even unconscious. Therefore, different codes can be encoded by dividing the long code and the short code during encoding, which is called doing something and not doing anything, thereby achieving the purpose of reducing the code rate.
5 Digital TV multiplexing system
The source-encoded image signal is sent to a multiplexer for multiplexing with the digital audio signal and then sent to the channel encoder.
There is no multiplexer in the analog TV system, and the video and audio signals are transmitted separately. However, in the digital TV, the data bit stream sent by the encoders such as video, audio, and auxiliary data is processed and combined into a single serial bit. Stream, for channel coding and modulation. The receiving end is just the opposite of this process, and the TV signal data is packaged to make it scalable, hierarchical, and interactive.
6 Digital TV channel codec and modulation and demodulation
The source code is compressed to eliminate data redundancy, and achieves the matching of the source code rate and the channel capacity, and solves the possibility of transmission. The purpose of digital TV channel codec and modulation and demodulation is to improve the anti-interference ability of the signal through error correction coding, network coding, equalization and other technologies to ensure the reliability of the transmitted signal. The process of channel coding is to insert some symbols into the source data stream to achieve the purpose of error determination and error correction at the receiving end. Therefore, it is a contradiction with source coding. System designers must consider maximizing effectiveness and reliability in limited bandwidth.
This style is a wet and dry Drum Vacuum Cleaner. Just as its name implies,it can use not only in wet place,but also in dry place. So it will let your cleaning more easily. This Vacuum Cleaner is also having big collection bin capacity,it will let your cleaning time longer. It also has free sliding wheels that will let your cleaning more relaxed. It has strong suction power,too. Please use it securely. Now please see some pictures blow.


Wet & Dry Drum Vacuum Cleaner, Drum Vacuum Cleaner
Ningbo ChinaClean Household Appliances Manufacture Co., Ltd. , http://www.chinaclean-elec.com