Workflow Activiti6 eBook:
Workflow Activiti6 instructional video:
Introduction to Activiti and Spring Boot Integration
When starting a new project, the first step is setting up the development environment. This involves selecting the appropriate technical stack, determining framework versions, and ensuring compatibility between different components. After this tedious setup, you need to configure the project, ensure it runs smoothly, and then share the environment with your team. Unfortunately, even if everything works on your machine, others may still face issues, leading to wasted time and frustration. These initial tasks are common in every project and often consume a lot of effort.
Inspired by frameworks like Ruby on Rails and Node.js, the Java EE community needed a more streamlined approach to reduce the complexity of project setup. This led to the introduction of Spring Boot, which simplifies the process of building applications. With Spring Boot, many configuration steps are automated—dependencies, server setups, and basic code structures are all pre-configured. All you need to do is add the required Spring Boot dependencies using a build tool like Maven or Gradle, and your application will run right away without worrying about version conflicts.
Spring Boot supports both Maven and Gradle as build tools. Maven is widely used and relies on the pom.xml file to manage project configurations. Gradle, on the other hand, uses Groovy-based scripts and offers good compatibility with older tools like Ant. Since I prefer Maven, this book will use it throughout. At the time of writing, the latest official version of Spring Boot was 1.5.4, which requires Maven 3.2 or higher.
Download and Install Maven
Apache Maven is a powerful project management tool that streamlines the build process. It stores all project-related information in the pom.xml file, making it easier to manage large and complex projects through its inheritance features.
One of Maven’s most useful features is dependency management. You simply declare the libraries your project needs in the pom.xml, and Maven automatically downloads and includes them along with their dependencies. This integration with Spring Boot makes it much faster to set up a functional development environment.
The Maven version used in this book is 3.5. You can download it from the official Maven website. After downloading and extracting the files, add the bin directory to your system’s environment variables, as shown in Figure 16-9.
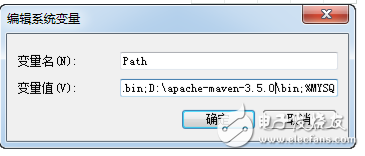
Figure 16-9 Modifying system environment variables
Once the setup is complete, open the command prompt and type "mvn -version" to verify the installation. The output should display the current Maven version. By default, Maven stores downloaded JARs in the local repository, typically located at C:\Users\username\.m2\repository.
Earlier versions of Eclipse required additional plugins for Maven support, but recent versions include built-in Maven tools. However, you can still configure Eclipse to use your own installed Maven version, such as 3.5.
Note: When importing a Maven project into Eclipse, make sure to select the "Existing Maven Project" option, as shown in Figure 16-10.
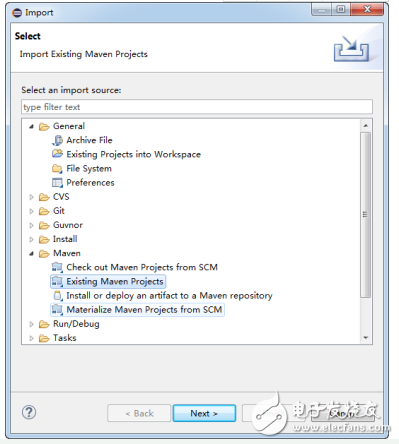
Figure 16-10 Importing a Maven project
Develop Your First Web Application
In this example, we’re using Spring Boot version 1.5.4. To begin, create a new Maven project in Eclipse, following the steps shown in Figures 16-11 to 16-13.
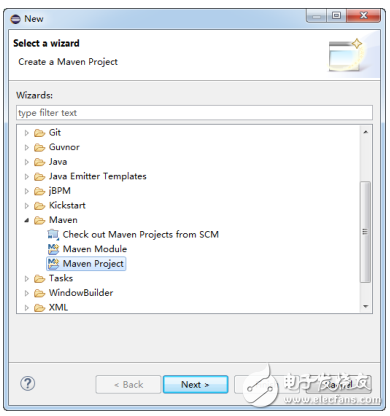
Figure 16-11 Creating a new Maven project
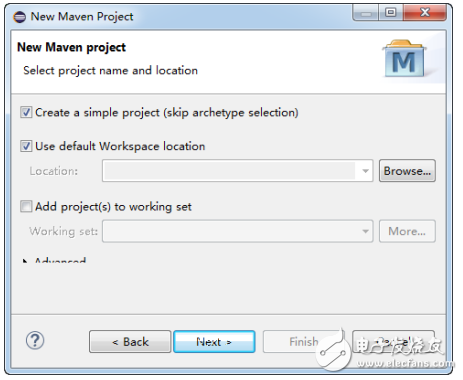
Figure 16-12 Creating a new Maven project
When creating the project, be sure to select “Create a simple project†to start with the most basic structure. This ensures a clean and manageable setup for your first Spring Boot application.
Auger Bearing Seat,Auger Bearings,Auger Hanger Bearings,Bearing Seats
Changzhou Youeryou Trading Co., Ltd. , https://www.farmpartssupplier.com