1 Introduction
Wireless Sensor Network (Wireless Sensor Network, WSN) is an intelligent private network that consists of a large number of sensor nodes with specific functions through self-organizing wireless communication method to transfer information to each other and coordinately complete specific functions. Sensor networks are generally deployed in harsh environments or in areas where it is difficult to get involved. It is almost impossible to replace node batteries or supplement energy. Therefore, the design of energy-efficient routing protocols is of great significance to wireless sensor networks. At present, the proposed WSN routing protocols mainly include two types of plane routing protocols and hierarchical routing protocols. Among them, the hierarchical routing protocols based on cluster structure are the hot spots of current research at home and abroad.
1 Related research
The primary goal of WSN clustering routing protocol design is to form a reasonable network structure through efficient clustering algorithms, prevent network connectivity decline through proactive energy management, and extend the life cycle of the network. The most typical wireless sensor network clustering routing protocol is the LEACH protocol. People have also developed many improved clustering routing protocols based on the LEACH protocol. The EECS (Energy Efficient Clustering Scheme) protocol is one of the classic improved algorithms.
1.1LEACH agreement
LEACH is the representative of distributed clustering protocol. Each node generates a random number from 0 to 1. If this number is less than the threshold, the node broadcasts that it is a cluster head to the entire network. The formula for calculating the threshold is:
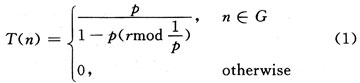
In the formula: p is the percentage of cluster heads to all nodes, that is, the initial probability that a node is elected as a cluster head, the actual cluster head probability floats up and down with p as the center; r is the current round of the cycle; G is the nearest 1 / p There is no set of nodes in the round that has been elected as the cluster head. It can be seen that the node selected as the cluster head will not become the cluster head in the next round, while the probability of the node generating a random number less than T (n) increases with the other nodes, so the node is elected as the cluster head The probability also increases. After the successful cluster head node broadcasts the elected message, other nodes decide which cluster to join according to the strength of the cluster head broadcast signal. Because the cluster heads are randomly selected, the LEACH protocol cannot guarantee that the cluster heads are evenly distributed in the network, and the nodes choose which clustering algorithm to join according to the principle of minimum communication cost, but they cannot guarantee the load balance of the clusters.
1.2 EECS agreement
As mentioned earlier, in algorithms such as LEACH, the node chooses which cluster to join according to the principle of minimum communication cost of its own, which cannot guarantee the load balance of the cluster, and does not consider the problem of excessive energy consumption of the cluster head far away from the base station. In response to these problems, EECS proposes a new communication cost formula (2) to determine which cluster a node joins:
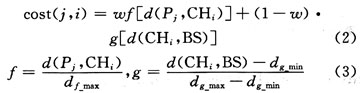
Where: cost (j, i) is the cost of node Pj joining cluster head i; d (Pj, CHi) is the distance from node to cluster head. The f sub-function in equation (3) ensures that the communication cost between the node and the cluster head is minimized; d (CHi, BS) is the distance from cluster head i to the base station, and the g sub-function in equation (3) ensures that the cluster head i is minimized The communication cost to the base station; the setting of the weight value w is a compromise between the energy of the member nodes and the energy consumption of the cluster head according to the specific application, and the goal is to maximize the network life cycle. The node Pj selects the cluster head i with the smallest cost (j, i) to join, so as to ensure the load balance of each cluster head. Experimental results show that the network life cycle of the EECS protocol has increased by more than 30% compared to the LEACH protocol.
2 Description of the problem
The essence of the EECS algorithm is that in the cluster head selection stage, the node with the largest remaining energy is always selected as the cluster head; in the clustering stage, the distance between the ordinary node and the cluster head and the distance between the cluster head and the base station are jointly considered. Its innovation lies in: only a small number of nodes participate in the election of cluster heads; broadcast messages in a local scope, the election process does not iterate; the remaining energy of the nodes is used as the election parameters; and a load balancing strategy between cluster heads is designed.
Problems in the EECS protocol:
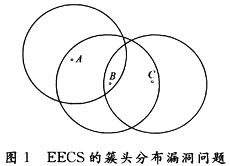
(1) In the clustering stage, the EECS algorithm allows candidate nodes to broadcast the election message COMPETE_HEAD at the same time, which is likely to cause cluster head distribution loopholes. As shown in Figure 1, node C is within B's election radius; node B is within A's election radius, and the remaining energy is A> B> C. In this case, when C receives the election message of B and quits the election, B receives the election message of A and quits the election. This will cause a local cluster head distribution loophole.
(2) The communication cost of the EECS algorithm in the clustering stage only considers the distance between the ordinary node and the cluster head, and the distance between the cluster head and the base station, and does not consider the remaining energy of the cluster head. This will cause premature death of some cluster head nodes with relatively little remaining energy.
In view of the problems in the EECS protocol, the ADEECS (Advanced EECS) protocol is proposed. This algorithm uses the contention delay method in the cluster head election stage, and a new communication cost calculation formula is designed in the cluster stage.
Outdoor Rental Led Display is waterproof design with IP65 front and IP54 back side, high brightness up to 6500cd/m2. You can disassemble cabinets, modules and power supplies without any tools. Easy to replace any parts, such as module, power supply and receiver. Both Neutrik and Harting power, signal connectors available. Linsn and Novastar control system. Outdoor waterproof SMD 3535 and 2727 LED lamps. High refresh rate and brightness. low power consumption. Safe and stable products.
Pixel pitch from P3.9mm, 4.8mm P5.9mm and P6.2mm. Packed in waterproof flight case for easy transportation. 220-110V power input and DVI,HDMI,SDI,DP signal input.
Curve installation is available.Inner and outer both up to 10°.
Excellent heat dissipation and noiselessness with ultra no fans.
Macromolecular flexible mask with glareless surface and better contrast ratio.
Intelligent LCD monitor for indicating working time and temperature.
Equipped with multifunctional video processor to get better image quality and scale resolution.
Automatic color calibration, larger viewing angle, wider range of audience, to meet the delicate color requirements.
Excellent thermal performance..
Save time:build quick, fast maintain, easy to loading or unloading.
Outdoor rental panel is Lightweight design, less workload. Save time and cost. Easy transportation.



Outdoor Rental Led Display,Outdoor Rental Led Screen,High Resolution Led Display,Led Stage Display
Shenzhen Bako Vision Technology Co., Ltd. , http://www.rentalleddisplays.com