The Internet of Things is an important part of the new generation of information technology. Its English name is "The Internetofthings". As the name suggests, "the Internet of Things is the Internet connected by things."
This has two meanings: First, the core and foundation of the Internet of Things is still the Internet, which is an extended and extended network based on the Internet. Second, its client extends and extends to any item and item for information. Exchange and communication. Therefore, the Internet of Things is defined as information sensing devices such as radio frequency identification (RFID), infrared sensors, global positioning systems, laser scanners, etc., to connect any item to the Internet in accordance with a contractual agreement for information exchange and communication. A network that enables intelligent identification, location, tracking, monitoring, and management of items.
At this stage, the Internet of Things is a local application network that is formed by means of various information sensing technologies and information transmission and processing technologies so that the state of the managed object (person or object) can be perceived and recognized. In the future, the Internet of Things is a huge network that connects these local application networks through the Internet and communication networks, forming a huge network of people and things, things and things. It is the infrastructure that perceives China and perceives the earth.
A sensor is a physical device or biological organ that detects and senses external signals, physical conditions (such as light, heat, humidity) or chemical components (such as smoke) and transmits the detected information to other devices or organs.
Sensors are common in everyday production, and they can change some physical quantities into electrical signals. For example, a microphone and a horn are a pair of voice sensors. In addition to the sensors that are used daily, there are many types of sensors. These sensors are rarely used, so their price is very high, which is why this has hindered the development of the Internet of Things. The sensor can be sound, light, pressure, vibration, speed, weight, density, hardness, humidity, temperature, image, voice, electric wave, chemistry; or gas flow rate, flow rate, pressure, composition; or liquid flow rate, flow rate , composition; or the amount, weight, hardness, etc. of the solid.
2. Electronic label (ID)Electronic tags are new technologies developed in the last century and have gained many applications, such as barcodes used by supermarkets to identify goods. Existing electronic tags include barcodes, two-dimensional codes, magnetic cards, contact IC cards, contactless cards, and radio frequency identification (RFID).
RFID (Radio Frequency IDenTIficaTIon) technology, also known as electronic tag, radio frequency identification, is a communication technology that can identify specific targets and read and write related data through radio signals without establishing a mechanism between the system and a specific target. Or optical contact.
3. Telecom networkA telecommunications network is a public facility of a telecommunications system and refers to a collection of nodes and links that provide connections between two or more specified points to establish telecommunication services and information between these points.
The telecommunications network has long been used by humans, and now the most used are the transmission of various information such as voice, text, music, pictures, and images. The information transmission of the Internet of Things has its unique place. Compared with the daily use of voice, text, music, pictures, and image transmission, the information transmission of the Internet of Things is more of a small amount of data transmission and a large amount of data transmission. It is as small as a few bits per month, such as gas meter reading; large to continuous transmission of large images, such as traffic monitoring, while medium-sized information transmission is relatively rare. This puts forward new requirements for communication. In order to achieve high-efficiency IoT communication, the communication industry needs to make new standards and new access devices to meet the needs of various communication of the Internet of Things. The existing communication networks include cable, optical cable, microwave, Bluetooth, infrared, WiFi, WINMX, mobile communication (2G, 3G, 4G), and satellite.
4, data processingThe data collected by the Internet of Things is for a variety of purposes. To meet different needs, the data needs to be processed by the computer. These processes often include summary summation, statistical analysis, threshold judgment, professional calculation, and data mining.
5, display systemImages and information collected by the Internet of Things often need to be displayed directly or calculated to be displayed on a computer or a large screen. Common display conditions include images, graphs, and curves.
6, the alarm systemInformation collected by the Internet of Things often requires direct alarm or alarm after computer processing. Common alarm forms are sound, light, electricity (telephone, SMS). A system that can alert when a selected parameter deviates from a preset limit value.
7, control execution systemSome Internet of Things are not only required to acquire signals, process signals, store signals, but also be required to issue control commands. The preset execution device specified by the network command performs the action by specifying the instructions of the preset execution device to achieve the control purpose.
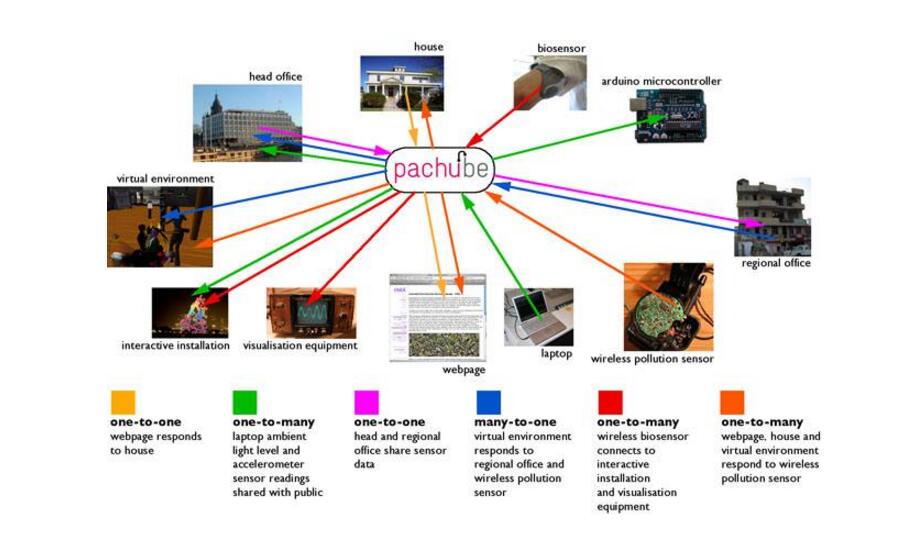
The technical system framework of the Internet of Things includes the perception layer technology, network layer technology, application layer technology and public technology:
Perceptual layerData collection and sensing are mainly used to collect physical events and data occurring in the physical world, including various physical quantities, identification, audio, and video data. Data acquisition of the Internet of Things involves technologies such as sensors, RFID, multimedia information collection, QR codes and real-time positioning. Sensor network networking and collaborative information processing technology realize short-distance transmission of data acquired by data acquisition technologies such as sensors and RFID, self-organizing networking and collaborative information processing of multiple sensors on data.
2. Network layerAchieve a wider range of interconnected functions, can transmit the perceived information without barriers, high reliability, and high security. It requires sensor networks to be integrated with mobile communication technologies and Internet technologies. After more than ten years of rapid development, technologies such as mobile communication and the Internet have matured and can basically meet the needs of data transmission of the Internet of Things.
3. Application layerThe application layer mainly includes an application support platform sublayer and an application service sublayer. The application support platform sub-layer is used to support information collaboration, sharing, and interworking between industries, applications, and systems. The application service sub-layer includes industrial applications such as intelligent transportation, smart medical, smart home, intelligent logistics, and smart power.
4. Public technologyPublic technology is not at a specific level of IoT technology, but is related to the three layers of the IoT technology architecture. It includes identification and resolution, security technology, network management, and quality of service (QoS) management.

The most basic feature of the Internet of Things is the provision of "Ubiquitous ConnecTIvity" with ten basic functions.
Online monitoring: This is the most basic function of the Internet of Things. The Internet of Things business is generally focused on centralized monitoring and supplemented by control.
Positioning traceability: generally based on GPS (or other satellite positioning, such as Beidou) and wireless communication technology, or rely solely on the positioning of wireless communication technologies, such as mobile base station based positioning, RTLS and so on.
Alarm linkage: mainly provides event alarms and prompts, and sometimes provides linkage function based on workflow or Rule Engine.
Command and dispatch: command, dispatch, and dispatch functions based on time scheduling and event response rules.
Plan management: Dispose of events generated by things based on pre-defined regulations or regulations.
Security and privacy: Due to the importance of IoT ownership attributes and privacy protection, IoT systems must provide corresponding security mechanisms.
Remote maintenance: This is a service that IoT technology can provide or enhance, mainly for enterprise product after-sales networking services.
Online upgrade: This is a means to ensure the normal operation of the IoT system itself, and is also one of the means of automatic after-sales service of enterprise products.
Leading the desktop: Mainly refers to the Dashboard or BI personalized portal. After the multi-layer filtering and refining the real-time information, the responsible person can realize the “a clear view†of the whole situation.
Statistical decision-making: Refers to data mining and statistical analysis of networked information, providing decision support and statistical reporting functions.

Internet of Things is widely used in intelligent transportation, environmental protection, government work, public safety, safe home, intelligent fire protection, industrial monitoring, environmental monitoring, street lighting control, landscape lighting control, building lighting control, square lighting control, elderly care, personal Health, flower cultivation, water monitoring, food traceability, enemy investigation and intelligence gathering.
Shenzhen ChengRong Technology Co.,Ltd. , https://www.laptopstandsuppliers.com