Laser TV (LASER TV) uses a semiconductor pumped solid-state laser working substance to generate continuous lasers of three wavelengths of red, green and blue as a light source of a color laser television, and controls a three-primary laser scanning image through a television signal. Its color gamut coverage can theoretically be as high as 90% of the gamut of the human eye [1]. This is a new level of 62% gamut coverage for LED TVs.
Laser TV principle features
The traditional color television uses the three primary color electron beams to strike the fluorescent screen line by line according to the law of the video signal, so that the fluorescent screen forms a colored spot. Using the residual visual effect of the human eye allows us to see the color image of continuous motion. This traditional color camera must be equipped with a cathode camera tube, even if the ultra-thin color TV must have a liquid crystal display, a plasma display, etc. [z0l. The mainstream TV types now include CRT TVs, LCD TVs, plasma TVs, and rear projection TVs. The cRT TV is a display using a cathode ray tube (Cathode RayTube), which has the advantages of large viewing angle, high color reproduction, extremely short response time, and low price. However, its huge and cumbersome structure has become a bottleneck for its development, and it is difficult to exceed 29 inches. It consumes a lot of power and does not meet the current energy-saving standards. In addition to special occasions, it is gradually withdrawing from the historical stage. Liquid crystal (LcD) TV is a display that uses liquid crystal controlled transmittance technology. It needs a white backlight to control the liquid crystal transmittance to control the backlight to transmit different colors through the red, green and blue color filters. Most of the current LCD backlights are cold cathode fluorescent lamps (CCFLs), which have a color gamut of only about 70% of CRT displays, and the displayed images are far less vivid than CRT displays. A plasma television (PDP) is a display device that uses gas discharge, and a large number of plasma chambers are arranged to form a screen. The inside of the plasma chamber is filled with an inert gas such as an atmosphere, and ultraviolet light is generated when the battery is energized, and the red, green and blue primary color phosphors in the excitation chamber emit visible light. It has the characteristics of high brightness, bright color and no electromagnetic interference, but it has the problem of burnt screen and altitude pressure, and it is difficult to achieve high resolution on large screen. The laser has good monochromaticity and high color purity. Compared with other existing displays (CRT, LCD, PDP, etc.), laser TV has obvious advantages, development prospects and potential value.
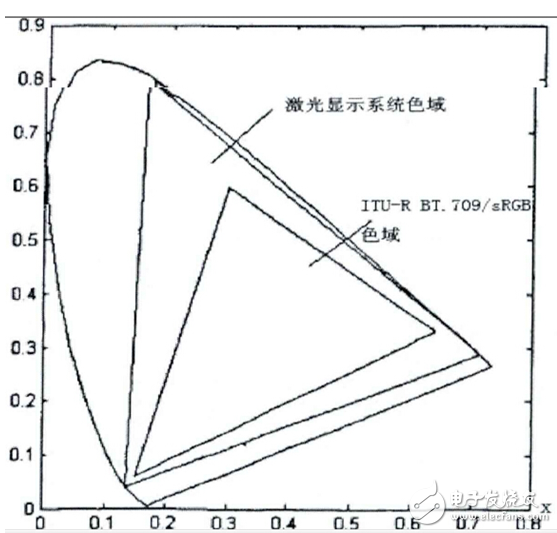
Laser TV technology is a new type of color TV display technology emerging in the 1990s. Due to the characteristics of laser, it has more advantages than other display technologies: (1) large screen, high brightness; (2) color gamut, height Saturated color for optimal color conversion. The size of the gamut reflects the size of the set of colors that the color system can contain. The wider the color gamut of the display device, the more colors that can be displayed and the more vivid the picture. The color gamut of the display device can be visually reflected on the CIE1931 chromaticity diagram developed by the International Commission on Illumination, which is represented by a polygon surrounded by primary color points. Figure 1-1 shows a wide color gamut display device - the laser display system and the color gamut of the standard color gamut ITU-RBT.709/SRGB currently used in the video field. Since the three primary color systems are used, the color gamut of both is triangular. The area covered by the outermost tongue-shaped spectral curve in the figure represents all the colors visible in nature. It can be seen intuitively that the color range covered by the standard color gamut is quite narrow, and the wide color gamut display device is incomparable compared with the traditional display device. The color rendering advantage. In the normal PAL system, the color gamut coverage is about 33.2%, and the laser display device color gamut can reach about 1.9 times. The closer the primary color of the display device is to the tongue curve, the larger the color gamut, and the narrower the spectral width of the male color is.
(3) It has unlimited depth of focus, can achieve high resolution, can be displayed on different materials (water curtain, fog screen, screen, etc.) and any shape surface, no matter whether the laser illuminates the screen at any angle, there is no distortion [4]; (4) High contrast (up to 150,000:1); (5) Fiber-optic light guide, multi-channel projection and satellite distribution, the light source can be separated from the projection head, and the operation is convenient. Therefore, it is one of the most promising technologies for achieving large screen and high definition display. Laser projection TV is a strong competitor in the 21st century TV market.
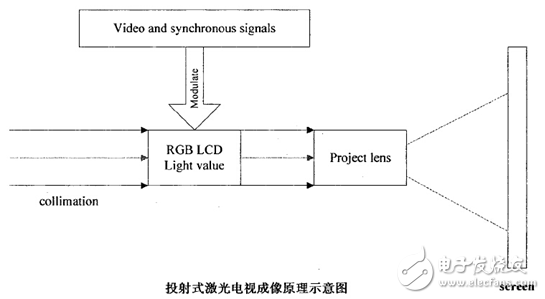
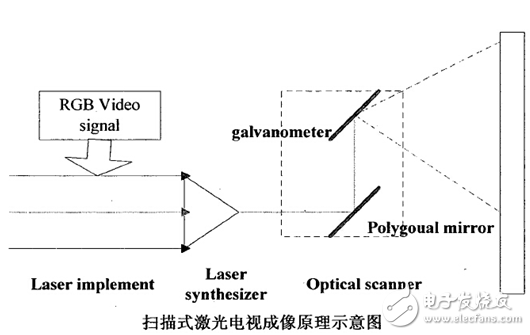
The imaging of the projection laser TV is similar to the principle of liquid crystal display, and the imaging principle is as shown. The light source of the ordinary projection display is ordinary white light, which is divided into three primary colors by a dichroic prism. The projection type laser television replaces the ordinary light source with red, green and blue three-color lasers, and then the laser is collimated and expanded to be projected. on the screen. The three primary color signals and the line sync signal separated by the television receiver are sent to cPu, and are controlled by CPu to control the luminous flux of each pixel of the liquid crystal, and finally imaged on the liquid crystal screen.
The laser television set described below uses a semiconductor pumped solid-state laser working substance to generate three kinds of lasers of three wavelengths of red, green and blue as a light source of a color laser television. After decoding, the television signal is stored in an image storage system, respectively. The image storage system extracts the luminance and chrominance signals, and the signal passes through the color management system to obtain a new RGB driving signal and transmits the driving signal to the LCOS display system, and directly projects the laser beam onto the screen to display a color image, mainly by laser and color management. System, LCOS display system, screen and other components [6]. as the picture shows:
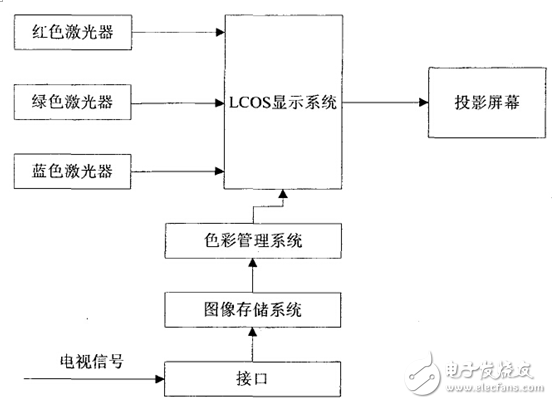
The beams emitted by the red, green and blue lasers are modulated by the optical engine and projected onto the LCOS spatial modem. The TV signals are stored in the buffer of the color management system via the DVI standard interface. The color management system processes the color signals and is suitable. The color signal of the laser display is passed to the LCOS display system and the image is projected onto the screen.
Integrated Rimless LED Panel Light includes round and square two shape frame. We are the manufacturer of producing energy saving interior lighting. These trimless led panels has built-in driver and external driver. The frame shell is made of PC material. There are three color temperatures with cool white, warm white and natural white of panel lights. It has both concealed and surface mounted installation way. The unique features of led trimless light are: CRI>80, PF>0.5. These panels are mainly apply to home, office and school, etc.
Integrated Rimless Surface Mounted Led Panel Light
Led Panel rimless Light,Interior Led Integration Light ,Led Integrated Light ,Round Rimless Integrated Lamp
Jiangmen Lika Lighting Electrical Appliances Co., Ltd , https://www.lika-led.com